Tools and Resources
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use forestresearch.gov.uk, remember your settings and improve our services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
Typical symptoms: leaf necrosis
Infected shoots (buds and young stems) and leaves of plants become necrotic. Entire tufts of foliage often wilt at the end of the shoots and then desiccate. Leaf necrosis occurs in many  infected species. In rhododendron, infected leaves often show blackening down the mid-vein and stalk (IMAGE: CIMG0861 severe dieback of rhododendron caused by P. kernoviae).
infected species. In rhododendron, infected leaves often show blackening down the mid-vein and stalk (IMAGE: CIMG0861 severe dieback of rhododendron caused by P. kernoviae).
Shoot tip dieback and leaf wilt of Rhododendron ponticum infected with P. kernoviae,
Cornwall, UK, 9 Aug 2005
Beech and oak: bleeding canker
Bark invasion by P. kernoviae In European beech (Fagus sylvatica) kills extensive areas of inner bark, often extending 10 m or more up the stem. This necrotic zone oozes a black, sticky fluid hence the phrase bleeding canker (IMAGE CIMG0907: Trunk of beech tree with bleeding cankers caused by Phytophthora kernoviae). Two English oak trees (Quercus robur) have also picked up infections from neighbouring host rhododendron bushes. These trees have also developed bleeding cankers.
host rhododendron bushes. These trees have also developed bleeding cankers.
Our monitoring of infected trees suggests that the bleeding cankers are not contagious, and the trees may recover from infection.
Bleeding canker caused by P. kernoviae on beech,
May 2006
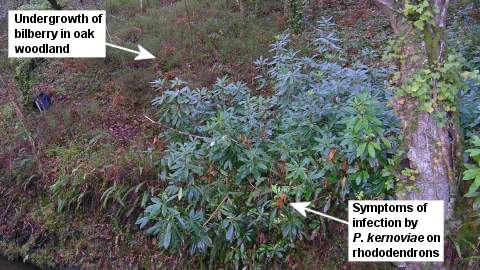
Bilberry (Vaccinium myrtillus)
Studies by Forest Research found P. kernoviae infecting plants of bilberry (Vaccinium myrtillus) in oak woodland and also open heathland in Cornwall. Bilberry is a native plant to Britain. It grows in lowland and upland heathlands, but can also be found in some woodlands, grasslands and peat bogs.
Symptoms include stem blackening and necrotic leaves, although the affected leaves are quickly shed.


Magnolia: leaf spot
A wide range of different magnolia species and hybrids have been infected by P. kernoviae, picking up the infection from affected rhododendrons in the same garden. Our research shows that P. kernoviae can persist on infected tissues over winter a nd then re-infect the new flowers and leaves that are formed the following spring. The most common symptom in Magnolia is leaf spot; some species also show bud blast and blossom blight (IMAGE: P kernoviae infection of magnolia foliage).
nd then re-infect the new flowers and leaves that are formed the following spring. The most common symptom in Magnolia is leaf spot; some species also show bud blast and blossom blight (IMAGE: P kernoviae infection of magnolia foliage).
Magnolia tree foliage infected with P. kernoviae,
Cornwall, UK, 22 Oct 2004
Diagnosis
The general symptoms of P. kernoviae infection make it difficult to diagnose without laboratory testing. If you find a rhododendron or tree exhibiting these symptoms, please contact our Tree Health and Disease Diagnostic Advisory Service. We may recommend you send us leaf or tissue samples so we can screen for P. kernoviae, P. ramorum and other possible pathogens.
More information
If you suspect a plant has P. kernoviae or a similar infection, please report your sighting using the Forestry Commission’s Tree Alert form.
| Latin name | Common name | Native range | Symptom expression |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Magnolia species | Magnolia amoena | – | China | Leaf spot |
| Magnolia cylindrica | Yellow mountain magnolia | China | Leaf spot and bud blast | |
| Magnolia delavayi | Chinese evergreen magnolia | China | Leaf blight | |
| Magnolia kobus | Kobus magnolia | Japan | Leaf spot and bud base death | |
| Magnolia liliiflora | Lily magnolia | China | Leaf spot | |
| Magnolia mollicomata ‘Lanarth’ | – | China | Leaf spot and bud blast | |
| Magnolia salicifolia | Willow-leafed magnolia | Japan | Leaf spot | |
| Magnolia sargentiana | Sargent’s magnolia | China | Leaf spot | |
| Magnolia sprengeri | Sprenger’s magnolia | China | Leaf spot | |
| Magnolia stellata | Star magnolia | Japan | Leaf spot | |
| Magnolia wilsonii | Wilson’s magnolia | China | Leaf necrosis and blossom blight | |
| Magnolia hybrids | Magnolia x soulangeana | Saucer magnolia | Japan | Leaf spot |
| Magnolia x brooklynensis (M. acuminata x M. liliiflora) |
Evamaria cucumber tree | Leaf spot | ||
| Magnolia Gresham hybrid ‘Joe McDaniel’ (M. soulangeana x M. veitchii) |
– | Leaf spot | ||
| Magnolia Gresham hybrid ‘Sayonara’ (M. soulangeana x M. veitchii) |
Sayonara magnolia | Japan | Leaf spot | |
| Magnolia x lobneri ‘Leonard Messel’ (M. soulangeana x M. veitchii) |
Leonard Messel magnolia | Japan | Leaf spot, blossom blight and bud blast |
Cookies are files saved on your phone, tablet or computer when you visit a website.
We use cookies to store information about how you use the dwi.gov.uk website, such as the pages you visit.
Find out more about cookies on forestresearch.gov.uk
We use 3 types of cookie. You can choose which cookies you're happy for us to use.
These essential cookies do things like remember your progress through a form. They always need to be on.
We use Google Analytics to measure how you use the website so we can improve it based on user needs. Google Analytics sets cookies that store anonymised information about: how you got to the site the pages you visit on forestresearch.gov.uk and how long you spend on each page what you click on while you're visiting the site
Some forestresearch.gov.uk pages may contain content from other sites, like YouTube or Flickr, which may set their own cookies. These sites are sometimes called ‘third party’ services. This tells us how many people are seeing the content and whether it’s useful.