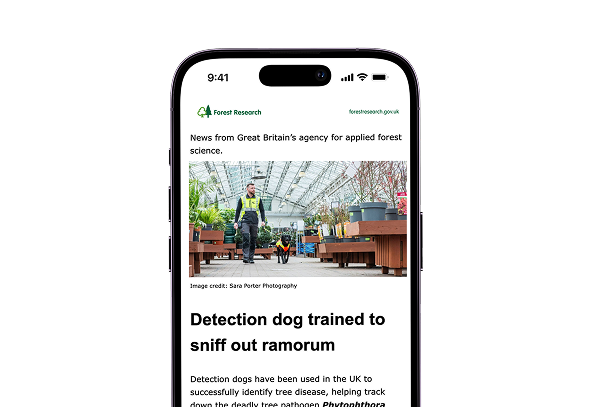
News
Read the latest news and features from Forest Research, and subscribe to our mailing list for updates directly to your inbox.
Read the latest news and features from Forest Research, and subscribe to our mailing list for updates directly to your inbox.
Subscribe to our mailing list to have the latest news, research and publications sent directly to your inbox.